Updating Software Remotely takes center stage, revolutionizing how businesses manage their digital infrastructure. As companies increasingly rely on technology, the need for efficient and secure software updates has never been more critical. Remote software updates not only streamline operations but also minimize downtime and bolster security, ensuring that organizations can adapt swiftly in a dynamic marketplace.
By leveraging various modern tools, businesses can implement remote updates that are both effective and time-saving. This approach allows for seamless scheduling across multiple devices, empowering IT teams to maintain optimal performance and security without the need for constant on-site intervention.
Importance of Updating Software Remotely
Remote software updates have become a cornerstone for modern businesses, ensuring that their systems are always equipped with the latest features and security enhancements. This process not only streamlines operations but also plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity of networked systems across geographically dispersed environments. As technology continues to advance, the necessity of updating software remotely is more vital than ever.Timely updates delivered remotely can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
They allow organizations to deploy upgrades across multiple devices without the need to physically access each one. This capability minimizes interruptions to business processes and maximizes productivity, ensuring that employees can focus on their core tasks without the burden of downtime or disruptions.
Benefits of Remote Software Updates for Businesses
Remote software updates provide several advantages that are essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. One of the primary benefits is the reduction of operational downtime, which is critical for businesses that rely on continuous service delivery.
- Continuous Service Availability: By implementing updates remotely, businesses can schedule updates during off-peak hours, thereby minimizing the impact on daily operations. This ensures that services remain available to customers without interruption.
- Resource Optimization: Remote updates reduce the need for IT personnel to travel on-site, allowing them to allocate their time and resources more effectively. This optimizes workforce deployment and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, maintaining software across a larger number of devices can become cumbersome. Remote updates facilitate the seamless rollout of necessary updates across all devices within the organization, no matter where they are located.
Minimizing Downtime through Remote Updates
Minimizing downtime is a critical objective for businesses, and remote updates play a pivotal role in achieving this goal. This approach allows for the rapid deployment of patches and updates necessary to address vulnerabilities and system bugs.
“Timely updates can prevent potential downtime that may arise from system failures or cyber threats.”
Some strategies that highlight how remote updates minimize downtime include:
- Automated Scheduling: Many remote update systems offer automated scheduling, allowing updates to be rolled out during non-business hours, thereby reducing user disruption.
- Instant Rollback Options: In case an update creates issues, remote systems typically provide instant rollback options, allowing businesses to revert to a previous stable state quickly.
- Real-time Monitoring: IT teams can monitor the implementation of updates in real time, ensuring that any arising issues are addressed immediately, further reducing potential downtime.
Security Enhancements Achieved through Timely Remote Updates
Security is a top priority for any organization, and remote software updates are a crucial component in fortifying defenses against cyber threats. With the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, timely updates can significantly enhance the security posture of an organization.
For companies looking to optimize their resources, exploring aquilon erp can be a game-changer. This comprehensive software solution integrates various business processes, enabling better data management and reporting. By adopting such innovative systems, organizations can enhance productivity and make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
“In the realm of cybersecurity, the most effective defense is often a proactive approach through timely updates.”
Implementing Client Portals via RMM can significantly enhance communication and efficiency between service providers and clients. These portals centralize information, making it easier for clients to track their service requests and updates. By leveraging this technology, businesses can improve client satisfaction while streamlining their operations.
The security enhancements offered by remote updates include:
- Patch Management: Regularly scheduled updates ensure that all security patches are applied promptly, mitigating vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
- Compliance Assurance: Many industries require compliance with specific regulations regarding software security. Remote updates help organizations stay compliant by ensuring that systems are up to date with the latest security protocols.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Remote update systems can integrate real-time threat intelligence, allowing businesses to respond to emerging threats quickly and effectively by deploying necessary security updates immediately.
Methods for Implementing Remote Software Updates: Updating Software Remotely
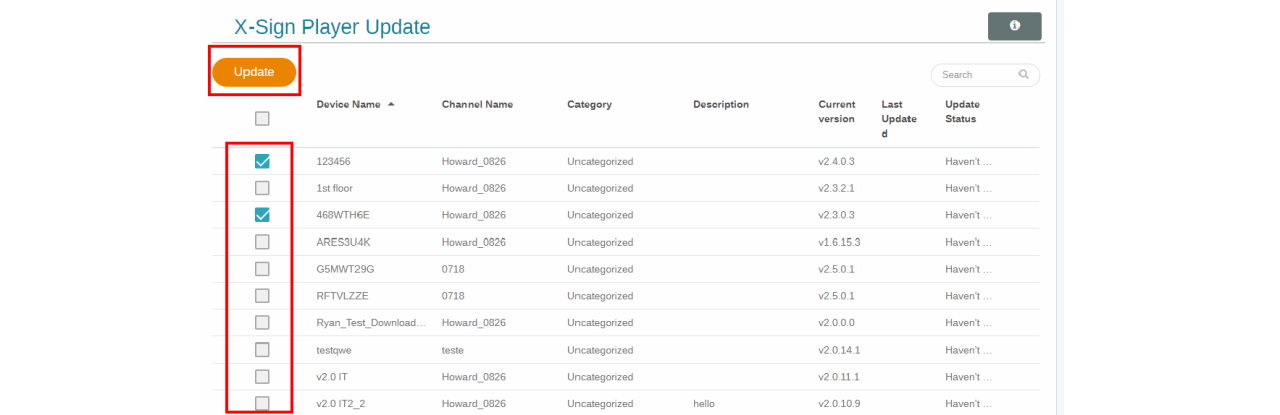
Implementing remote software updates effectively is crucial for maintaining system integrity, security, and performance across multiple devices. Various methods and tools are available to ensure that updates are managed seamlessly, minimizing downtime and user disruption.One of the primary tools used for managing remote updates includes specialized software solutions that facilitate the deployment of updates across diverse environments. These tools allow IT administrators to push updates centrally, monitor compliance, and ensure that all devices are running the latest software versions.
Tools for Managing Remote Updates
A range of tools exists to assist in managing remote software updates, each offering unique features suited to different organizational needs. The following tools are widely recognized in the industry:
- Microsoft Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): A widely used tool that enables IT administrators to manage the distribution of updates released through Microsoft Update to computers in a corporate environment.
- System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM): This comprehensive management tool allows for patch management, software distribution, and remote control across various devices, enhancing administrative control over update processes.
- Jenkins: An open-source automation server that can be configured to automate the deployment of software updates, particularly useful in DevOps environments.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus: This cloud-based solution automates the deployment of patches and updates for operating systems and third-party applications, ensuring compliance and security.
Scheduling Updates Across Multiple Devices
Scheduling updates effectively is critical to minimizing disruption and ensuring that all devices are consistently maintained. Different approaches can be adopted to suit varying organizational needs:
- Time-Based Scheduling: This method involves setting specific times for updates to occur, typically during off-peak hours when user activity is low, to reduce operational impact.
- Event-Triggered Scheduling: Updates can be triggered by specific events, such as after a user logs off or at system startup, ensuring updates are applied without user intervention.
- Rolling Updates: This approach allows updates to be deployed gradually across different groups of devices, ensuring that any issues can be identified and addressed without affecting the entire user base.
- Policy-Based Updates: Organizations can create policies that dictate how and when updates occur based on device type, user role, or location, providing a tailored update experience.
Step-by-Step Guide for Setting Up Automated Update Processes
Setting up an automated update process streamlines the management of software updates significantly. The following steps provide a straightforward approach to establishing an automated system:
- Choose the Right Tool: Select a software management tool that meets your organization’s specific needs for remote updates.
- Configure Update Settings: Access the tool’s settings to define how updates should be handled, including scheduling and notification preferences.
- Establish Update Policies: Create policies that dictate how different devices and users will receive updates, allowing for fine-tuned control over the update process.
- Test Updates: Before rolling out updates widely, conduct a pilot test on a small group of devices to identify any potential issues.
- Deploy Updates: Initiate the automated deployment process, ensuring that all configurations and schedules are set correctly.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly check the update deployment status and compliance across devices, adjusting policies as necessary to improve effectiveness.
“Automated update processes not only save time but also enhance security by ensuring that all devices are kept up-to-date with the latest patches and features.”
Challenges in Remote Software Updates
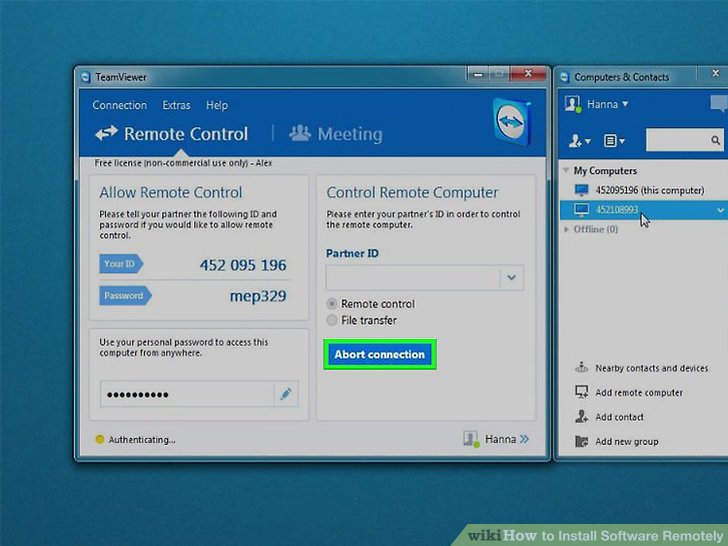
The process of updating software remotely presents a unique set of challenges that organizations must navigate to ensure successful implementation. These challenges can range from technical issues to user resistance, all of which can hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of remote updates. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for organizations looking to streamline their update processes and maintain security and functionality within their systems.
Common Obstacles Faced During Remote Updates
Remote software updates can encounter several common obstacles, which can significantly impact their success. Identifying these issues is the first step in developing strategies to mitigate them.
- Network Reliability: Poor or unstable internet connections can interrupt the update process, leading to incomplete installations or failures.
- Device Compatibility: Variability in device configurations and operating systems can result in compatibility issues, causing certain updates to fail.
- Insufficient Resources: Remote updates often require adequate bandwidth and storage. Lack of these resources can lead to slow updates or system freezes.
- Security Risks: Remote updates pose security challenges, particularly if the update files are intercepted or compromised during download.
Strategies for Troubleshooting Update Failures
When remote software updates fail, implementing effective troubleshooting strategies is essential. Organizations can employ various methods to diagnose and resolve issues quickly.
- Log Analysis: Reviewing update logs can provide insights into where the failure occurred, allowing for targeted fixes.
- Rollback Procedures: Having a rollback plan enables users to revert to the previous version of the software, minimizing downtime while troubleshooting.
- Test Environments: Setting up a controlled environment to test updates before deployment can help identify potential issues in a risk-free setting.
- Real-time Monitoring: Using monitoring tools to track update progress can help detect problems early and initiate immediate responses.
User Resistance to Remote Updates
User resistance is a significant challenge that many organizations face when implementing remote software updates. Employees may have concerns about the impact of updates on their work or fear changes to familiar processes.
- Communication: Clearly communicating the benefits of updates can help alleviate user concerns. Providing information on new features and security enhancements can encourage acceptance.
- Training Sessions: Offering training or informational sessions can empower users to feel more comfortable with changes and updates, showcasing how these updates improve their workflow.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing channels for users to express their concerns and feedback can foster a culture of collaboration, making users feel valued and understood.
- Flexibility in Scheduling: Allowing users to schedule updates at their convenience can reduce disruption and resistance, as they can choose times that minimize impact on their work.
Best Practices for Remote Software Management
Effectively managing remote software updates requires a structured approach, ensuring reliability and security while minimizing downtime. Organizations that adopt best practices in remote software management can enhance their operational efficiency and mitigate risks associated with software vulnerabilities. This section discusses essential strategies for successful remote software updates.
Checklist for Successful Remote Updates
A comprehensive checklist is vital for ensuring that remote software updates proceed smoothly and efficiently. The following points serve as a guideline to help teams manage updates effectively and avoid common pitfalls:
- Pre-update assessment: Verify compatibility and the necessity of the software updates before deployment.
- Backup critical data: Ensure that backups of essential data and configurations are in place to prevent data loss.
- Testing in a controlled environment: Conduct tests of the update in a non-production environment to identify potential issues.
- Clear documentation: Maintain up-to-date documentation regarding the update procedures and any changes being made.
- Schedule updates during off-peak hours: Minimize disruption by performing updates during periods of low user activity.
- Monitor update progress: Utilize monitoring tools to track the update process and identify any errors or concerns early.
- Post-update verification: Confirm that the updates are applied correctly and that the software is functioning as expected.
Importance of User Communication During Updates
Effective communication with users during software updates is crucial to ensure transparency and reduce frustration. Users should be informed about the update schedule, expected downtime, and any changes that will affect their work. This proactive communication fosters trust and prepares users for any necessary adjustments.Key aspects of user communication include:
- Advance notifications: Provide users with timely updates regarding when the software will be updated and how it may impact their workflows.
- Detailed update information: Share specifics about what changes the updates entail, including potential benefits and any new features.
- Support channels: Ensure users know how to reach support in case they experience issues after the update.
- Feedback mechanisms: Encourage users to report any problems encountered post-update, aiding in rapid resolution and continuous improvement.
Process for Validating the Success of Software Updates Remotely, Updating Software Remotely
Validating the success of remote software updates is a critical step in confirming that the updates have been applied correctly and that any new features or fixes are functioning as intended. An effective validation process typically involves several key steps:
- Automated testing: Implement automated testing procedures to quickly assess whether core functionalities are working after the update.
- User feedback collection: Solicit feedback from users to identify any issues that may not be detected through automated processes.
- Performance monitoring: Utilize performance monitoring tools to track the software’s functionality and identify any anomalies following the update.
- Log analysis: Review logs generated during and after the update for errors or warnings that may indicate issues.
- Rollback procedures: Prepare rollback plans in case significant issues arise, allowing for a quick return to the previous stable version.