Smart Alerts with RMM play a crucial role in modern IT environments, transforming how businesses monitor and manage their systems. By leveraging these intelligent notifications, organizations can swiftly respond to potential issues before they escalate, ensuring seamless operations and minimizing downtime.
Smart Alerts are designed to notify IT teams of critical changes within their infrastructure, whether it’s a sudden spike in network traffic or a drop in server performance. These alerts not only provide real-time insights but also help in preemptively addressing issues, showcasing their significance in Remote Monitoring and Management systems.
Smart Alerts Overview
Smart Alerts play a crucial role in Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) systems, enhancing the ability of IT professionals to maintain optimal system performance and security. By providing real-time notifications based on specific criteria, Smart Alerts are designed to minimize downtime and proactively address issues before they escalate into significant problems. This systematic approach to alerting ensures that IT teams can focus their efforts on resolving critical issues and improving overall service delivery.The significance of Smart Alerts lies in their predictive nature and the automation of monitoring tasks that would otherwise require constant human oversight.
For businesses looking to optimize their operations, exploring the latest erp top solutions is essential. These systems offer comprehensive features that cater to various organizational needs, from finance to supply chain management. Implementing a robust ERP system can lead to better decision-making and improved productivity across all departments.
In IT environments, Smart Alerts are utilized in a variety of scenarios, including system performance monitoring, security breach detection, and compliance assurance. For instance, if a server exceeds its CPU usage threshold, a Smart Alert can be triggered to notify the IT team to investigate potential overloads or misconfigurations. Similarly, when unusual login attempts are detected, alerts are generated to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity.
In the world of business management, utilizing tools like aquilon erp can significantly enhance operational efficiency. This software streamlines processes, making it easier for companies to manage resources effectively, and adapt to changing market demands. By integrating advanced functionalities, businesses can stay competitive and agile in their respective industries.
Types of Alerts and Trigger Conditions
Understanding the types of alerts generated by Smart Alerts and the conditions that trigger them is essential for effective RMM implementation. The alerts can typically be categorized into several types, each serving a distinct purpose in maintaining IT operations. These alerts are based on predefined thresholds, system behaviors, or anomalies detected within the network.The following highlights the primary types of Smart Alerts and their trigger conditions:
- Performance Alerts: Triggered when system resources such as CPU, memory, or disk usage exceed specified limits. For instance, a CPU usage alert might be activated when usage surpasses 85% for an extended period, indicating potential bottlenecks.
- Security Alerts: Generated in response to suspicious activities, such as multiple failed login attempts or unauthorized access from unfamiliar IP addresses. This type of alert is critical for maintaining network security and compliance.
- Service Availability Alerts: These alerts notify IT teams of service outages or degradations, such as a server going down or an application becoming unresponsive. For example, if a web server is down for more than five minutes, an alert can be triggered to inform the support team.
- Compliance Alerts: Triggered when systems fall out of compliance with regulatory standards. This could involve alerts related to missing security patches or configuration changes that violate established policies.
- Event-Based Alerts: Activated by specific events, such as changes in configuration or software installations. An example includes alerts generated when a critical software patch is applied, ensuring that system updates are monitored closely.
“Smart Alerts transform reactive IT management into proactive monitoring, significantly enhancing an organization’s ability to mitigate risks and improve service uptime.”
By leveraging Smart Alerts within RMM systems, organizations can bolster their operational resilience and ensure that potential disruptions are addressed swiftly and effectively. Each alert serves as a vital communication tool, guiding IT professionals in navigating the complexities of modern IT environments.
Benefits of Implementing Smart Alerts
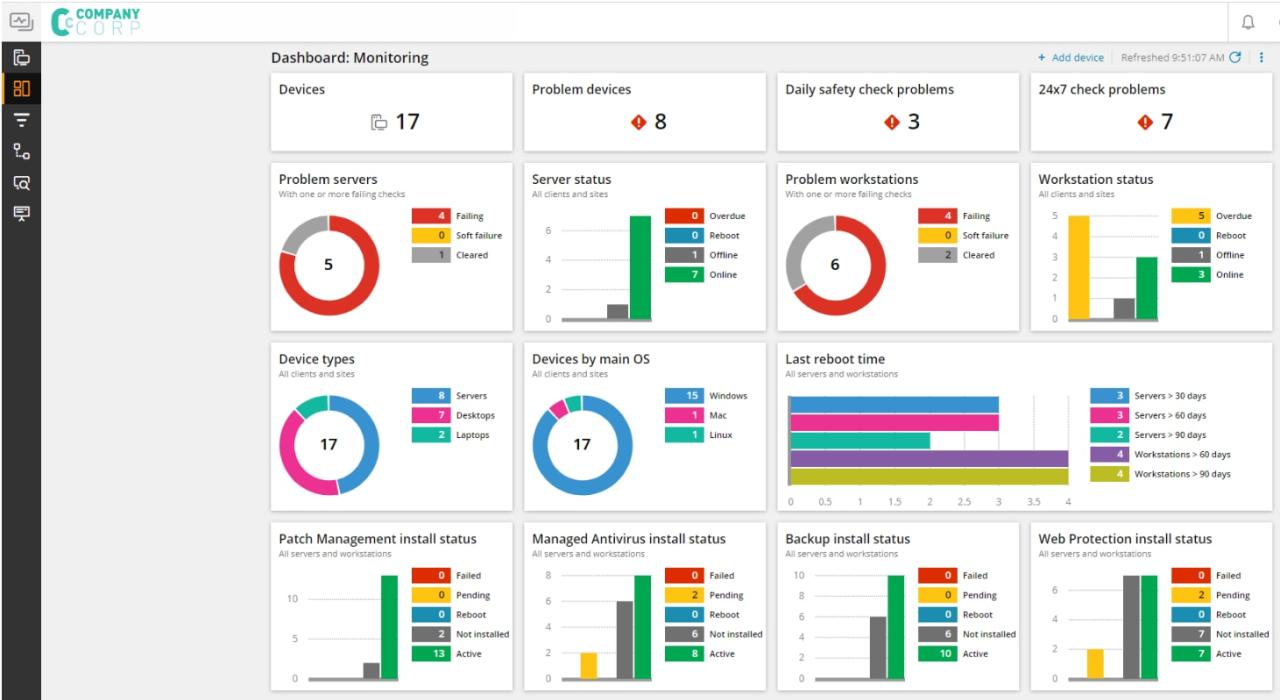
Integrating Smart Alerts into Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions offers a transformative approach for businesses to streamline their operations. Organizations are increasingly faced with the challenge of maintaining system uptime and ensuring that potential issues are addressed before they escalate into significant problems. Smart Alerts provide timely notifications that enable proactive responses, ultimately enhancing operational effectiveness.The advantage of Smart Alerts extends beyond immediate notifications.
By allowing businesses to anticipate and mitigate risks before they culminate in downtime, organizations can unlock substantial cost savings and improvements in overall efficiency. The value of such systems is evident in their ability to minimize interruptions and maintain productivity.
Cost-Saving Benefits Through Reduced Downtime
Minimizing downtime is crucial for any business, as even short periods of unavailability can lead to significant financial losses. Smart Alerts assist organizations in addressing issues swiftly, which directly translates into cost savings. The cost of downtime can be staggering; according to a study by Gartner, the average cost of IT downtime is estimated to be around $5,600 per minute.
This figure underscores the importance of having an efficient alert system in place. Key advantages of implementing Smart Alerts include:
- Early Detection: Smart Alerts facilitate early detection of potential failures, allowing IT teams to intervene before issues escalate into downtime.
- Reduced Recovery Time: With timely alerts, businesses can substantially decrease the time taken to restore services, thus minimizing operational disruptions.
- Improved Resource Allocation: Proactive monitoring and alerts allow IT resources to be allocated more efficiently, focusing on strategic initiatives rather than reactive firefighting.
“The reduction of downtime through timely alerts can save businesses thousands, if not millions, in lost revenue.”
Improvements in Operational Efficiency
The integration of Smart Alerts not only results in cost savings but also significantly enhances operational efficiency. Case studies and statistics reveal that organizations employing Smart Alerts have seen marked improvements in their workflows and productivity levels. For instance, a leading technology firm reported that after implementing Smart Alerts, they reduced their incident response time by 30%. This shift allowed teams to focus on core business objectives rather than constantly dealing with unexpected system failures.
Additionally, a financial services company showcased a 25% increase in overall service availability, attributing this success directly to the implementation of Smart Alerts in their RMM strategy. Such statistics illustrate the profound impact these alerts can have on an organization’s operational capacity.Businesses that invest in Smart Alerts not only position themselves for cost-effective operations but also foster a culture of efficiency and reliability, which are vital in today’s competitive landscape.
Best Practices for Configuring Smart Alerts: Smart Alerts With RMM
Establishing an effective Smart Alerts system within your RMM tool is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal performance. By carefully configuring these alerts, organizations can respond quickly to issues and maintain operational efficiency. This section will explore best practices for effectively setting up Smart Alerts, customizing thresholds, and implementing a monitoring checklist to enhance accuracy over time.
Steps for Setting Up Smart Alerts
The initial phase of configuring Smart Alerts involves several important steps that set the foundation for effective monitoring and response.
1. Define Objectives
Clearly Artikel the goals of your Smart Alerts. Whether it’s monitoring system health, security vulnerabilities, or network performance, having specific objectives helps streamline the setup process.
2. Select Relevant Metrics
Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your objectives. Metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network latency are critical for system health monitoring.
3. Configure Alert Triggers
Set triggers based on the selected metrics. For instance, you might configure an alert to trigger when CPU usage exceeds 85% for more than 5 minutes.
4. Prioritize Alerts
Classify alerts into categories (critical, warning, informational) to manage response priorities effectively. This classification aids teams in addressing the most pressing issues first.
5. Assign Notification Channels
Determine how alerts will be communicated. Options include email, SMS, or integrations with communication platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
Customizing Alert Thresholds
Adjusting alert thresholds according to specific organizational needs enables a tailored approach to monitoring. Organizations differ in system capacity, user behavior, and operational objectives, which makes customization essential.
Analyze Historical Data
Review past performance data to identify normal operating ranges for each metric. This analysis allows organizations to set realistic thresholds that minimize false positives.
Engage Stakeholders
Collaborate with teams across departments to gather insights on critical performance thresholds. Different teams may have unique thresholds based on their operational functions.
Incremental Adjustments
Start with conservative thresholds and gradually adjust them based on real-time data and feedback from alert responses. This iterative approach helps refine alert accuracy.
Regularly revising thresholds based on new data and changing conditions ensures that alerts remain relevant and effective.
Checklist for Monitoring and Adjusting Alerts
To maintain the effectiveness of your Smart Alerts system, a regular monitoring and adjustment process is essential. The following checklist serves as a guide for ongoing evaluation:
Review Alert Performance
Monthly review of alert logs can highlight trends, such as frequent false positives or overlooked issues.
Solicit Feedback
Regularly gather feedback from team members who respond to alerts. Their insights can inform necessary adjustments and improvements.
Update Thresholds
Adjust thresholds based on new operational metrics or changes in infrastructure.
Test Alerts
Periodically test alert configurations to ensure they are functioning as intended. This practice can uncover any potential issues before they impact operations.
Document Changes
Keep a record of all adjustments made to alerts and thresholds. Documentation provides clarity on the evolution of your monitoring strategy.By implementing these best practices, organizations can maximize the effectiveness of their Smart Alerts within RMM tools, ensuring that they remain responsive and relevant to changing operational demands.
Challenges and Solutions in Smart Alerts Management

Managing Smart Alerts in Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) systems presents a unique set of challenges that can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of IT operations. As organizations increasingly rely on automated alerts to manage their systems, it becomes crucial to address the common issues that arise in this domain. One primary challenge is alert fatigue, where teams become desensitized to frequent notifications, leading to missed critical alerts.
Additionally, the volume of alerts can overwhelm staff, resulting in confusion about which alerts require immediate attention and which can be deprioritized. It is essential to ensure that alerts are actionable to facilitate a swift response. Training teams effectively is vital in improving incident response times, as well as enhancing overall system reliability and performance.
Overcoming Alert Fatigue, Smart Alerts with RMM
Alert fatigue can be a significant barrier to effective incident management. It occurs when the sheer volume of alerts leads to desensitization, causing important alerts to be overlooked. To combat this issue, organizations can implement the following strategies:
- Prioritize Alerts: Classify alerts based on severity and impact, ensuring that critical incidents are highlighted and addressed first.
- Custom Alert Thresholds: Adjust alert thresholds tailored to specific environments or applications, reducing the number of non-critical alerts generated.
- Alert Consolidation: Implement mechanisms that consolidate similar alerts into a single notification, minimizing noise while retaining necessary information.
- Regular Review and Tuning: Periodically review alert configurations and adjust them to reflect changes in the environment or business priorities.
By utilizing these strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the noise generated by alerts, allowing teams to focus on what truly matters.
Ensuring Actionable Alerts
Creating actionable alerts is essential for effective incident response. Alerts should be designed to provide clear context and actionable insights. Here are key approaches to ensure alerts are actionable:
- Contextual Information: Include relevant details about the alert, such as affected systems, possible causes, and suggested remediation steps, to empower teams to act swiftly.
- Integration with Incident Management: Use tools that integrate alerts directly into incident management systems, facilitating streamlined workflows and documentation.
- Alert Automation: Automate responses for common alert types, reducing the need for manual intervention and expediting resolution times.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a feedback loop where teams can indicate the effectiveness of alerts, leading to continuous improvement in alert configurations.
Actionable alerts not only enhance the speed of incident response but also improve overall operational efficiency.
Training Teams for Effective Response
Training IT teams to respond effectively to Smart Alerts is critical for improving incident response times. Comprehensive training programs should cover the following areas:
- Understanding Alert Context: Educate teams on the significance of various alerts and the context in which they occur, enabling better prioritization and response.
- Simulated Incident Response: Conduct regular drills that simulate real-world incidents, allowing teams to practice their response strategies in a controlled environment.
- Documentation and Knowledge Sharing: Develop a centralized knowledge base containing documentation, best practices, and previous incident analyses to aid team members in responses.
- Continuous Learning: Encourage ongoing training sessions and workshops to keep teams updated on new tools, technologies, and threat landscapes.
By investing in training, organizations can ensure that their teams are equipped to respond effectively to Smart Alerts, ultimately enhancing incident management capabilities.