How to Migrate RMM is a critical topic for businesses looking to optimize their remote monitoring and management processes. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, a seamless transition to a new RMM tool can significantly enhance operational efficiency and service delivery. This guide walks you through the essential steps to ensure a successful migration, from meticulous planning and risk assessment to selecting the right solution and training users.
It’s not just about moving data; it’s about creating a holistic strategy that minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity. By addressing potential challenges and understanding the importance of user adoption, you can pave the way for a smoother transition to a more effective RMM system.
Planning the Migration Process: How To Migrate RMM
A successful migration of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools requires meticulous planning and execution. It involves several critical steps to ensure that the transition is smooth and minimizes disruption to operations. This phase sets the foundation for the entire migration process, allowing businesses to leverage new tools effectively while addressing potential obstacles.Understanding the essential steps in the migration process can help organizations streamline their efforts.
Effective planning not only involves identifying necessary resources and personnel but also requires assessing the current infrastructure and capabilities. Below are key steps to consider during this phase.
Essential Steps for a Successful Migration
The migration process can be divided into actionable steps that facilitate a seamless transition. Each step is crucial and should be carefully executed to mitigate risks.
- Assessment of Current Infrastructure: Evaluate existing systems and identify what needs to be migrated, including configurations, settings, and data.
- Choosing the Right RMM Tool: Research and select an RMM tool that fits your organization’s needs, considering scalability, features, and user-friendliness.
- Involving Stakeholders: Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are involved in the planning phase to address varying needs and gain necessary buy-in.
- Developing a Migration Strategy: Create a comprehensive strategy that Artikels the migration process, including timelines, responsibilities, and communication plans.
- Training Employees: Provide training sessions for staff to familiarize them with the new RMM tool and its functionalities.
- Testing the Migration: Conduct a pilot migration to identify issues and refine the process before full implementation.
Identifying Potential Challenges and Risks
During the migration process, organizations may face various challenges that could hinder success. Recognizing these potential pitfalls in advance allows teams to develop contingency strategies.
To enhance efficiency, it’s crucial to Boost Productivity via RMM. Utilizing Remote Monitoring and Management tools allows teams to automate routine tasks, freeing up valuable time for more strategic initiatives. This approach not only increases operational efficiency but also fosters a more proactive work environment, leading to better overall outcomes.
- Data Loss: Risk of losing critical data during the transfer can be minimized by implementing backup solutions before migration.
- Downtime: Transitioning to a new RMM tool may result in temporary service interruptions. Proper planning can help schedule migration during off-peak hours.
- Integration Issues: Compatibility problems with existing systems can arise, making it essential to evaluate integration capabilities beforehand.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new tools. Engaging them in the process and providing adequate training can mitigate resistance.
Designing a Timeline for Each Phase of the Migration
A well-structured timeline is vital for keeping the migration process on track and ensuring all phases are adequately addressed. It provides clarity and helps manage expectations throughout the organization.
- Preparation Phase (1-2 weeks): Assess current systems, select an RMM tool, and secure stakeholder approvals.
- Training Phase (1 week): Conduct training sessions for users to familiarize them with the new tool.
- Pilot Migration (2 weeks): Execute a test migration to identify potential issues and refine the process.
- Full Migration (2-4 weeks): Transition all systems, data, and configurations to the new RMM tool.
- Post-Migration Review (1 week): Evaluate the success of the migration, address any outstanding issues, and gather feedback from users.
“A structured migration plan reduces risks and enhances the chances of achieving a successful transition.”
Understanding the importance of Monthly RMM Reports can significantly enhance your business strategies. These reports provide insights into system performance and help identify areas for improvement, making them an essential tool for effective decision-making. By regularly analyzing these reports, companies can streamline their operations and stay ahead of potential issues.
Selecting the Right RMM Solution
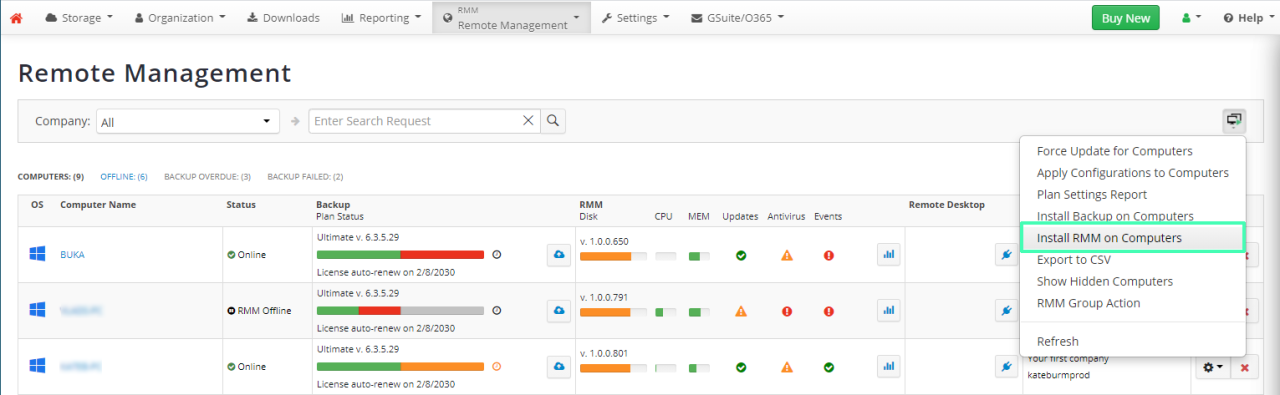
In the rapidly evolving tech landscape, selecting the right Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution is paramount for businesses aiming to enhance their IT operations. A well-chosen RMM solution not only streamlines processes but also boosts overall productivity, thereby providing a competitive edge.When evaluating RMM solutions, important factors such as features, pricing, and scalability must be considered. The right RMM platform should cater to the specific needs of a business while accommodating future growth.
Below is a comparison of some of the most popular RMM solutions available today, highlighting essential features and pricing structures.
Comparison of Popular RMM Solutions, How to Migrate RMM
The landscape of RMM solutions is diverse, with each provider offering unique features at different price points. Below is a detailed analysis of several leading RMM platforms, providing insights into their capabilities and suitability for various types of organizations:
| RMM Solution | Key Features | Pricing | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|
| ConnectWise Automate | Remote access, patch management, automation scripts | Starts at $75/month per technician | Highly scalable for growing MSPs |
| Datto RMM | Cloud-based management, integrated BDR, customizable dashboards | Pricing based on device count, approximately $100/month for 10 devices | Ideal for businesses of all sizes |
| SolarWinds RMM | Network monitoring, antivirus integration, ticketing system | Starts at $35/month per device | Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses |
| ManageEngine RMM | Patch management, asset management, mobile device support | $10/month per device with a minimum commitment | Flexible scalability options |
Criteria for Evaluating RMM Platforms
Selecting an RMM solution involves a careful assessment of multiple criteria, ensuring that the chosen platform aligns with organizational needs and goals. Here are key factors to consider:
- Feature Set: Evaluate the essential features provided, such as network monitoring, patch management, and reporting capabilities. A robust feature set enhances overall functionality.
- Pricing Structure: Consider both upfront and ongoing costs. Some platforms charge per device, while others may have a flat fee or tiered pricing based on usage.
- Ease of Use: The user interface should be intuitive, allowing technicians to navigate easily and perform tasks efficiently.
- Integration Capabilities: Analyze how well the RMM solution integrates with existing tools, such as ticketing systems and customer relationship management (CRM) software.
- Security Features: Given the rise in cyber threats, ensure the solution offers robust security measures, including encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Importance of Customer Support
Customer support is a critical factor in the effectiveness of an RMM solution. Efficient customer support can significantly reduce downtime and improve service delivery. Organizations should assess the following aspects:
- Response Time: Quick response times to inquiries and issues can mitigate potential disruptions in operations.
- Support Channels: Availability of multiple support channels (phone, email, chat) enhances accessibility for users.
- Resource Availability: Comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and community forums can aid users in troubleshooting common issues independently.
In conclusion, selecting the right RMM solution encompasses a thorough evaluation of features, pricing, and scalability alongside a keen focus on customer support and integration capabilities. This careful consideration ensures that organizations invest in a platform that not only meets their current needs but also supports future growth and operational efficiency.
Data Migration Strategies

Migrating data to a new Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) system is a critical step in ensuring a smooth transition. Selecting the right strategy for data migration can significantly affect the success of the migration process. Effective data migration not only helps in maintaining operational continuity but also safeguards the integrity of important business information.There are several established methods for transferring existing data to a new RMM system, each with its unique characteristics and suitability based on the specific requirements of the migration.
Methods for Transferring Data
Choosing the appropriate data migration method is key to ensuring a seamless transition to the new RMM solution. The main methods include:
- Direct Transfer: This method involves moving data directly from the old RMM to the new system. It is often the quickest method but requires thorough testing to ensure compatibility and integrity.
- Export and Import: Data is exported from the old RMM into a common format (like CSV or XML) and then imported into the new system. This method allows for more control over the data and can be beneficial when needing to clean or reorganize data during the transfer.
- Automated Migration Tools: Utilizing specialized software tools designed for RMM data migration can streamline the process. These tools often provide features for mapping, transforming, and validating data, reducing manual errors.
- Phased Migration: This approach involves migrating data in stages. It is particularly useful for larger datasets where a full migration at once may cause disruptions. Phased migrations allow you to test and validate data in smaller batches.
Checklist for Validating Data Integrity Post-Migration
After the migration process, ensuring that the data has been transferred accurately is crucial. A comprehensive checklist can help validate the integrity of the migrated data. Key points to consider include:
- Verify that all records from the old RMM system are present in the new system.
- Check for discrepancies in data formats (e.g., date formats, currency).
- Conduct random sampling of records to ensure data accuracy.
- Validate relationships between data sets, ensuring that linked data remains connected.
- Review the system logs for any migration errors or warnings.
- Confirm that user permissions and access controls are correctly applied.
Importance of Data Backup Before Migration
Backing up data before executing the migration is a fundamental practice that cannot be overlooked. It acts as a safety net, preventing data loss during the transition. The importance of data backup includes:
“A reliable backup ensures that you can recover your original data in case of issues during the migration process.”
Prior to migration, create a complete backup of the existing RMM data. This backup should be stored securely and tested to confirm its integrity. In the event of data corruption, loss, or migration errors, having a recent backup allows for easy restoration, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.Additionally, consider implementing a rollback strategy where, if significant issues arise post-migration, you can revert to the old RMM system without data loss.
This proactive approach can significantly enhance your confidence during the migration process.
User Training and Adoption
The successful implementation of a new Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) platform hinges significantly on effective user training and adoption. A well-structured training program not only equips users with the skills needed to navigate the new system but also fosters a positive attitude towards the transition. To ensure users feel confident and competent in using the new RMM platform, it is crucial to invest time and resources into their training and support.
Training Program Design
Creating a comprehensive training program tailored to the new RMM platform is essential for user preparedness. This program should include several key components:
- Initial Assessment: Evaluate the current skill levels of the users to tailor the training content accordingly. Understanding the baseline knowledge will help identify areas that require more focus.
- Module-Based Learning: Develop training modules that cover different functionalities of the RMM platform. Each module should focus on specific tasks, such as monitoring, reporting, and troubleshooting.
- Hands-On Workshops: Organize interactive workshops where users can practice using the platform in a controlled environment. This practical experience can significantly boost confidence and retention of information.
- Documentation and Guides: Provide comprehensive user manuals and quick-reference guides. These resources should be easily accessible for users to refer to as needed.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement a system for obtaining feedback on the training process. This allows for continuous improvement of the training program based on user experiences.
Best Practices for User Adoption
Ensuring user adoption and minimizing resistance is a crucial aspect of transitioning to a new RMM solution. Incorporating best practices can lead to a more seamless experience for all stakeholders involved.
- Communicate Benefits: Share clear information about how the new RMM platform will enhance their daily tasks and overall productivity. Highlighting specific improvements can motivate users to embrace the change.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage influential users early in the process to champion the new system. Their endorsement can facilitate broader acceptance among other team members.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Establish a support system that users can rely on during the transition. This could include a dedicated help desk or access to a knowledgeable resource person.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Help users understand that some adjustment time is necessary. Clearly defining what success looks like at various stages can alleviate anxieties about the change.
- Recognize and Reward Engagement: Acknowledge users who actively participate in the training and adoption process. Offering incentives can boost morale and encourage a positive attitude towards the new system.
Supportive Resources During the Transition
To facilitate a smooth transition, it is vital to ensure that users have access to supportive resources.
- Online Help Center: Create a robust online help center featuring FAQs, instructional videos, and troubleshooting guides. This resource should be continuously updated to reflect the evolving needs of users.
- Regular Check-Ins: Schedule follow-up sessions to address any challenges users face after the initial training. This ongoing engagement allows for timely support and reinforces learning.
- Peer Support Groups: Encourage the formation of user groups where individuals can share experiences, tips, and best practices. This collaborative environment can significantly enhance skills and confidence.
- Webinars and Live Demos: Offer regular webinars and live demonstrations of advanced features to deepen users’ understanding and showcase the platform’s capabilities.
- Access to Management: Ensure users have opportunities to provide direct feedback to management about their experiences and suggestions for improvement. This two-way communication fosters a sense of involvement and ownership.