erp edi serves as a pivotal mechanism in the contemporary business landscape, seamlessly connecting enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems with electronic data interchange (EDI). This integration is not just a technological advancement; it represents a strategic alignment that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity within organizations. Through the amalgamation of these systems, businesses can streamline operations, reduce errors, and foster stronger relationships with partners and customers.
Understanding the fundamental concepts of ERP and EDI is essential for grasping the myriad benefits of this integration. It encompasses key components that facilitate effective communication and data exchange, enabling organizations to adapt swiftly to market demands and maintain a competitive edge.
Understanding ERP EDI Systems

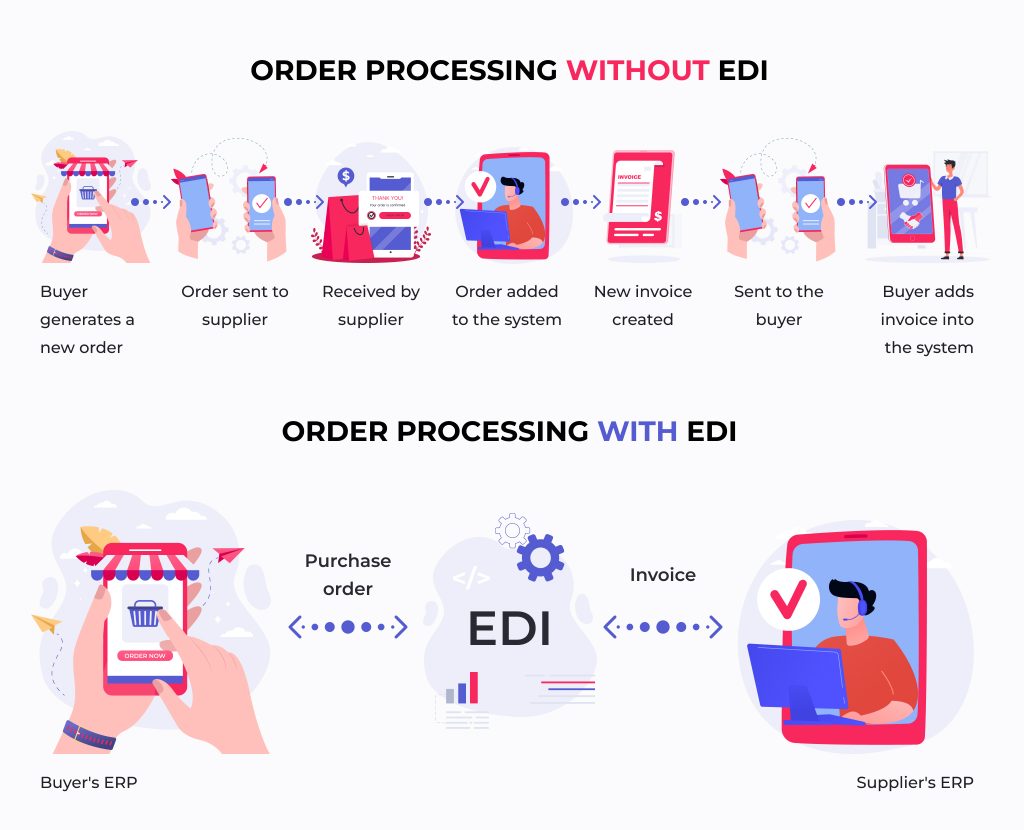
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) are pivotal in streamlining business processes and enhancing communication across various functional areas. ERP systems centralize data and facilitate management of business functions such as finance, supply chain, and human resources. Meanwhile, EDI enables the electronic exchange of data between organizations, allowing for real-time transactions and reducing the need for manual interventions.The integration of EDI within an ERP system offers numerous advantages, including improved accuracy, decreased processing time, and enhanced data management.
By automating data exchange, businesses can minimize errors that typically arise from manual data entry and ensure that critical information flows seamlessly between partners. This integration not only optimizes the order and inventory management processes but also strengthens relationships with suppliers and customers by ensuring timely and accurate information sharing.
For companies seeking to enhance operational efficiency, ax erp is a remarkable choice, offering features that facilitate better resource management. Similarly, the one erp platform presents a holistic approach to integrate various business functions, ensuring seamless collaboration among departments. Adopting these systems can significantly improve overall productivity and drive business success.
Benefits of Integrating EDI within an ERP System, Erp edi
Incorporating EDI into an ERP framework can lead to transformative benefits that significantly enhance operational efficiency. Some key advantages include:
- Increased Efficiency: Automating data exchange reduces the time spent on manual entry and reconciliation of documents.
- Cost Savings: Decreased paper usage and elimination of postage and processing costs lead to reduced operational expenses.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated systems minimize human errors, ensuring that data is consistent and reliable.
- Faster Processing: Orders and invoices can be processed significantly quicker, leading to improved cash flow and customer satisfaction.
- Better Compliance: EDI facilitates adherence to industry standards and regulations, streamlining the compliance process.
Key Components of an Effective ERP EDI System
To implement a successful ERP EDI system, various components must be carefully considered and integrated. These components work in tandem to ensure smooth operations and seamless data flows:
- EDI Standards: Adopting widely recognized standards such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT ensures compatibility across different systems.
- Integration Middleware: Middleware solutions allow for seamless data exchange between ERP systems and various EDI platforms, acting as a bridge between different technologies.
- Data Mapping: Effective mapping of data fields between the ERP and EDI systems is crucial for ensuring accuracy and consistency in data exchange.
- Monitoring and Reporting Tools: These tools help track the status of EDI transactions, ensuring all communications are processed correctly and allowing for quick issue resolution.
- Training and Support: Investing in training for staff ensures they are equipped to handle the EDI processes effectively, leading to better overall system utilization.
Integrating EDI into ERP systems not only promotes operational efficiency but also fosters stronger business relationships through reliable and timely communication.
Implementation Strategies for ERP EDI
Implementing ERP EDI systems in a business is a structured process that requires careful planning and execution. This integration is crucial for improving business efficiency, enhancing communication with trading partners, and automating processes. Successful implementation ensures that the organization can reap the full benefits of both ERP and EDI systems.The implementation of an ERP EDI system comprises several key steps, each essential for ensuring that the integration aligns with business objectives and operational requirements.
The following steps Artikel a systematic approach to effectively implementing an ERP EDI system.
Steps for Implementing ERP EDI
A well-defined implementation strategy is critical to the success of ERP EDI systems. The following steps serve as a guide for organizations looking to integrate these systems seamlessly:
- Assessment of Business Requirements: Understand the unique needs of the business. This step involves identifying the specific processes that will benefit from EDI integration.
- Selection of the Right EDI Solution: Evaluate and select an EDI solution that aligns with the organization’s ERP system and business goals.
- Establish Data Mapping: Define how data will flow between the ERP and EDI systems, ensuring compatibility and accuracy of information exchanged.
- Testing the Integration: Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues before going live. This phase ensures that all processes function as intended.
- Training Staff: Equip employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to operate the new system effectively, emphasizing the importance of user engagement during this phase.
- Go Live: Launch the ERP EDI system in a controlled manner, monitoring its performance and addressing any immediate challenges.
- Continuous Improvement: After implementation, regularly assess system performance and seek opportunities for enhancements based on user feedback and evolving business needs.
Best Practices for Selecting an ERP EDI Solution
Selecting the right ERP EDI solution is a pivotal step that can significantly influence the effectiveness of the implementation. Adhering to these best practices can aid in making an informed choice:
“Selecting an appropriate ERP EDI solution is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and fostering strong trading partner relationships.”
Implementing an integrated system is crucial for modern businesses, and one such solution is one erp. This platform streamlines various processes, fostering efficiency and collaboration. Additionally, organizations looking for a robust solution may consider ax erp , which provides comprehensive tools to manage resources effectively. Both options cater to distinct needs, ensuring that businesses can thrive in a competitive landscape.
- Compatibility with Existing Systems: Ensure that the ERP EDI solution integrates seamlessly with your current ERP software and other systems in use.
- Scalability: Opt for a solution that can grow with your business, accommodating increased transaction volumes and additional functionalities as needed.
- User-Friendliness: A solution that is easy to use will facilitate quicker adoption and reduce the learning curve for employees.
- Vendor Support and Reputation: Choose a vendor with a proven track record of reliable support and a reputation in the industry for excellence.
- Cost Consideration: Assess the total cost of ownership, including initial setup, ongoing maintenance, and any transaction fees associated with the solution.
Challenges and Solutions During Implementation
Implementing an ERP EDI system may present several challenges that could hinder the process. Recognizing these potential hurdles and understanding how to overcome them is crucial for a smooth transition.
“Anticipating challenges and having a plan in place to address them can significantly enhance the success of the implementation process.”
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to new technologies. Implementing a change management strategy that includes training and clear communication can alleviate concerns.
- Data Quality Issues: Poor data quality can impair the effectiveness of the integration. Establishing data governance practices ensures that data is accurate and consistent across both systems.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating diverse systems can be complex. Engaging experienced IT professionals or consultants can facilitate smoother integration.
- Compliance and Security Risks: Ensure that the chosen EDI solution complies with industry regulations and incorporates robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
Industry Applications of ERP EDI
The integration of ERP EDI (Enterprise Resource Planning Electronic Data Interchange) has become pivotal across various industries, facilitating seamless communication and data exchange. This technology not only streamlines operations but also enhances collaboration and efficiency within supply chains. Different sectors have unique requirements, and through the application of ERP EDI systems, organizations are able to address these needs effectively.In the manufacturing sector, ERP EDI solutions are instrumental in managing supply chain logistics, inventory control, and production scheduling.
By enabling real-time data exchange with suppliers and customers, manufacturers can optimize their operations and reduce lead times. In retail, ERP EDI systems facilitate inventory management, order processing, and customer relationship management, allowing for an agile response to market demands. The healthcare industry utilizes these systems to improve patient care management, streamline billing processes, and enhance the accuracy of medical data exchange.
Comparison of ERP EDI Usage Across Industries
Understanding how ERP EDI is utilized differently across sectors can provide insights into its versatility and effectiveness. Below is a comparison of its applications in manufacturing, retail, and healthcare:
- Manufacturing: ERP EDI systems in manufacturing allow for automated purchase orders and invoices, thus reducing manual errors and accelerating processing speed. For example, automotive manufacturers utilize EDI to communicate with suppliers regarding part specifications and delivery schedules.
- Retail: Retailers leverage ERP EDI to manage stock levels, process sales orders, and handle customer data efficiently. A prominent example is a major retail chain that implemented EDI to automate its reorder process, resulting in a 30% reduction in stock levels and improved cash flow.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, ERP EDI is crucial for managing patient records and billing. Hospitals have adopted EDI systems to transmit patient data securely, facilitating better coordination of care. A notable case is a healthcare provider that reduced billing cycle times by 40% after implementing EDI for claims submissions.
Case Studies of Successful ERP EDI Integrations
Several organizations across different industries have successfully integrated ERP EDI systems, showcasing the tangible benefits of this technology.
Case Study: A global electronics manufacturer integrated ERP EDI to enhance its supply chain efficiency, resulting in a 25% decrease in operational costs and improved supplier collaboration.
Case Study: A leading hospital network adopted ERP EDI to streamline its procurement processes, significantly reducing the time taken to process orders and improving patient service delivery.
Case Study: A large retail company implemented an ERP EDI system to improve order fulfillment rates, which led to a 15% increase in customer satisfaction and retention rates.
These examples illustrate how the effective implementation of ERP EDI systems can lead to enhanced operational efficiency and improved overall performance across various sectors.
Future Trends in ERP EDI Technology
The landscape of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is on the brink of significant transformation driven by emerging technologies. With advances in digital solutions, organizations are adapting to streamline their operations further, enhance decision-making, and improve customer satisfaction. Understanding these trends is essential for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge and optimize their ERP and EDI systems for the future.One of the most impactful changes anticipated in the ERP EDI domain is the integration of emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
These technologies are set to enhance data analytics capabilities, allowing for more accurate forecasting and better resource allocation.
Impact of Cloud Computing on ERP EDI Evolution
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in the evolution of ERP EDI systems by providing scalable resources, reducing operational costs, and enhancing accessibility. The shift towards cloud-based solutions enables organizations to deploy ERP EDI systems without significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. The advantages of cloud computing in ERP EDI include:
- Scalability: Businesses can easily scale services according to their needs, accommodating growth without significant additional costs.
- Accessibility: Cloud solutions allow remote access to ERP EDI systems, enabling teams to collaborate effectively regardless of location.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud providers often manage software updates, ensuring that businesses are always using the latest features and security enhancements.
- Cost Efficiency: Subscription-based pricing reduces the need for large capital expenditures, allowing organizations to allocate resources more efficiently.
Future of Automation within ERP EDI Processes
The future of automation within ERP EDI processes is set to revolutionize how businesses manage their transactions and data flow. Automation technologies, including Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI-enhanced workflows, are anticipated to streamline repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and increase operational efficiency. Key aspects of automation in ERP EDI include:
- Enhanced Data Entry: Automation minimizes the need for manual data entry, significantly reducing the risk of errors and improving data accuracy.
- Faster Processing Times: Automated processes can handle transactions at a much faster rate compared to traditional methods, leading to quicker order fulfillment and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Integration with Other Systems: Automation facilitates seamless integration between ERP, EDI, and other business systems, ensuring a unified and streamlined approach to managing business operations.
- Predictive Analysis: Utilizing AI, organizations can predict trends and automate decision-making processes based on real-time data analysis.
“The integration of AI and automation in ERP EDI systems is not just an upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses will operate in the future.”