MSP Pricing with RMM sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As Managed Service Providers (MSPs) navigate the complex landscape of pricing models, understanding the various approaches they employ—like flat-rate, per-device, and tiered pricing—becomes crucial. Each model comes with its own advantages and disadvantages, particularly when paired with Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) services, making it essential for businesses to grasp these nuances to make informed decisions.
Delving deeper, we explore the factors influencing MSP pricing with RMM, ranging from service levels to customer needs and market demand. The impact of RMM tools on operational costs and pricing strategies further complicates the equation, as the perceived value of common RMM features plays a significant role in pricing discussions. Additionally, budgeting for MSP services, including these costs, presents its own challenges, with pitfalls that many businesses encounter.
To assist in financial planning, we’ll Artikel typical service offerings and their associated costs, while also examining emerging trends and innovative strategies that leading MSPs are adopting in today’s rapidly evolving pricing landscape.
Understanding MSP Pricing Models: MSP Pricing With RMM
Managed Service Providers (MSPs) employ various pricing models to deliver their services effectively, particularly when it comes to Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM). The chosen pricing structure can significantly impact both the service provider’s profitability and the client’s satisfaction. Understanding these pricing models is essential for MSPs to align their service offerings with customer needs while maintaining a sustainable business.Different pricing models utilized by MSPs include flat-rate, per-device, and tiered pricing.
Each of these models presents unique advantages and disadvantages, especially regarding the provision of RMM services. A clear understanding of these models allows MSPs to choose the most appropriate one that aligns with their business strategies and their clients’ expectations.
The integration of erp automotive systems revolutionizes the automotive industry by streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency. This technology helps manufacturers manage everything from supply chain logistics to production schedules, ensuring that operations run smoothly and cost-effectively, which is crucial in a competitive market.
Pricing Models Overview
The following are the primary pricing models employed by MSPs, along with their respective benefits and drawbacks in relation to RMM services:
-
Flat-Rate Pricing:
With flat-rate pricing, MSPs charge a predetermined fee for a comprehensive set of services. This model simplifies budgeting for clients but may lead to under-service or over-service scenarios. -
Per-Device Pricing:
This model charges clients based on the number of devices being managed. While it allows for scalability, it may discourage clients from adding devices due to cost implications. -
Tiered Pricing:
Tiered pricing offers different service levels at varied price points. This flexibility can cater to diverse client needs, but may lead to complexity in service management.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pricing Models, MSP Pricing with RMM
Understanding the pros and cons of each pricing model helps MSPs make more informed decisions when it comes to pricing their services. The following points summarize the key aspects:
| Pricing Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Flat-Rate |
|
|
| Per-Device |
|
|
| Tiered |
|
|
“Choosing the right pricing model is crucial for MSPs, as it influences client retention and overall profitability in the competitive IT landscape.”
Factors Influencing MSP Pricing with RMM
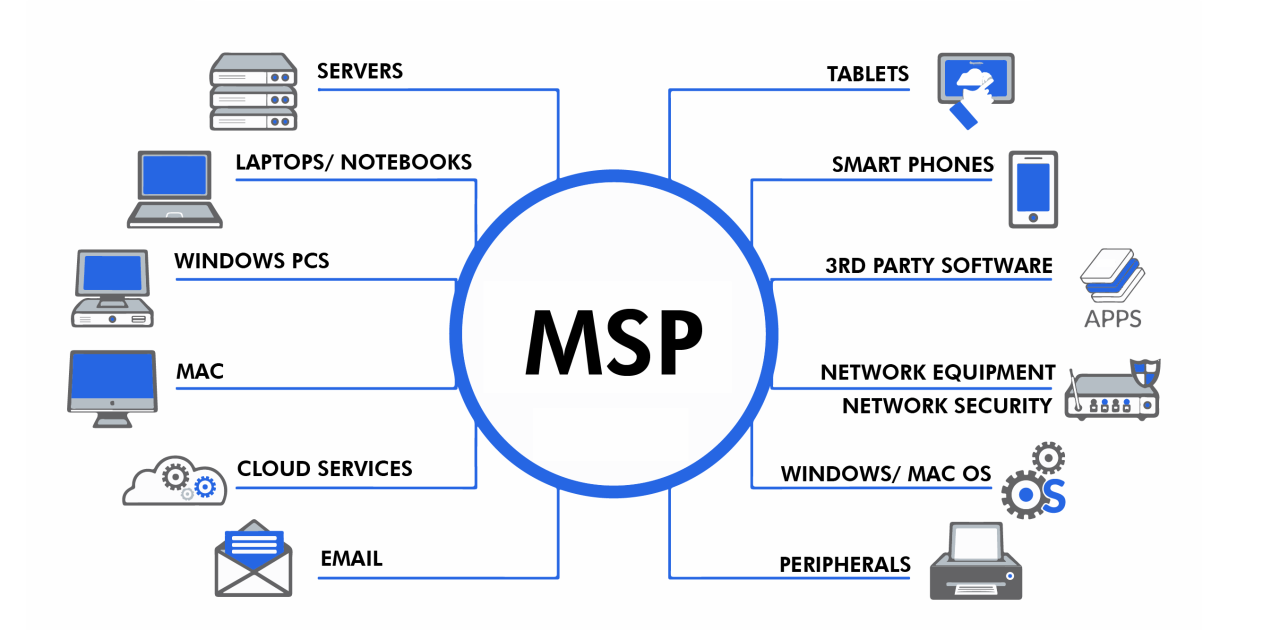
Pricing for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) utilizing Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools is influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these key elements is essential for MSPs to develop effective pricing strategies that align with their service offerings and customer expectations. The complexity of service levels, the specific needs of customers, and the ever-evolving landscape of market demand all play critical roles in determining pricing structures.Operational costs and pricing strategies for MSPs are directly impacted by the capabilities of RMM tools.
These tools not only automate many routine tasks but also provide advanced functionalities that can enhance service delivery and efficiency. MSPs must consider the costs associated with implementing and maintaining RMM tools, as these expenses will influence overall pricing models. Additionally, the features provided by RMM tools can greatly affect customer perceptions of value, which in turn plays a crucial role in pricing discussions.
Key Pricing Influencers
Several key factors influence the pricing of MSP services integrated with RMM solutions. Understanding these elements allows MSPs to tailor their offerings and pricing to best meet the needs of their clients.
- Service Levels: The depth and breadth of services provided, such as proactive monitoring, incident response, and compliance management, significantly impact pricing. Higher service levels often demand more resources and expertise, leading to increased costs.
- Customer Needs: Each client may have unique requirements based on their business size, industry, and existing infrastructure. Customizing services to meet these demands can result in different pricing tiers to accommodate diverse needs.
- Market Demand: The competitive landscape influences pricing strategies. An MSP operating in a market with high demand for RMM services may price aggressively to capture clients, while a saturated market may lead to price reductions to attract customers.
- Operational Costs: The costs associated with the RMM tools themselves, including licensing fees, maintenance, and training for staff, can affect pricing. MSPs need to ensure that these costs are factored into their pricing structures to maintain profitability.
Impact of RMM Tools on Pricing Strategies
RMM tools carry a significant weight in shaping the operational costs and overall pricing strategies of MSPs. Their integration can lead to streamlined operations and improved service delivery.The use of RMM tools allows for greater efficiency in managing client systems, which can reduce labor costs and enhance productivity. This operational efficiency enables MSPs to offer competitive pricing while maintaining margins.
However, the initial investment in RMM tools and ongoing maintenance must be balanced with the pricing offered to clients.
Common RMM Features and Their Value
When discussing pricing, it’s important to highlight the features of RMM tools that clients perceive as valuable. Each feature contributes to the overall service offering and justifies the pricing model.
- Automated Monitoring: Continuous system monitoring helps preemptively identify issues before they escalate, which can save clients time and money in the long run.
- Patch Management: Regular updates and patching for software and systems mitigate security vulnerabilities, enhancing client security posture.
- Remote Access: The ability to troubleshoot and resolve issues remotely reduces downtime and improves client satisfaction.
- Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reporting on system performance and usage can provide valuable insights for clients, helping them to make informed decisions.
Budgeting for MSP Services
When businesses consider Managed Service Provider (MSP) services, a critical aspect that often comes into play is budgeting. Understanding how to effectively allocate resources for these services, which may include Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM), can significantly impact an organization’s efficiency and financial health. This guide Artikels essential budgeting considerations, common pitfalls, and provides a structured overview of typical MSP service offerings and associated costs.
Key Budgeting Considerations for MSP Services
Budgeting for MSP services involves a comprehensive approach to understanding various cost factors. By evaluating the specific needs of the business, organizations can better anticipate the financial commitments involved. It is essential to consider the complexity of the IT environment, the level of support required, and any additional services that may be beneficial. The following points highlight critical considerations for effective budgeting:
- The size and scope of the business, including the number of devices and users that need support.
- Specific services required from the MSP, such as network security, data backup, or cloud services.
- Potential for future growth, which may necessitate scaling the services and associated costs.
- Understanding the pricing models of different MSPs to find a suitable fit for the budget.
- Including contingencies for unexpected expenses related to IT management and support.
Common Pitfalls in Estimating MSP Service Expenses
While budgeting, businesses often encounter several pitfalls that can lead to underestimated costs or unexpected financial strain. Recognizing these challenges can help in creating a more accurate budget. Key pitfalls include:
- Failing to account for all components of the MSP services, such as onboarding and training costs.
- Not considering fluctuations in demand for IT support, which may vary based on business cycles.
- Ignoring hidden fees or additional charges that some MSPs may impose for certain services.
- Overestimating the in-house capabilities and underestimating the need for outsourced support.
- Neglecting to regularly review and adjust the budget as the business evolves and needs change.
Typical MSP Service Offerings and Their Associated Costs
A well-structured overview of typical MSP service offerings can significantly aid in the budgeting process. The following chart Artikels common services provided by MSPs along with their average associated costs, which can vary based on factors such as service complexity and provider reputation:
| Service Offering | Average Monthly Cost |
|---|---|
| Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) | $100 – $300 per device |
| Network Security Solutions | $500 – $2,500 per month |
| Data Backup and Disaster Recovery | $200 – $750 per month |
| Help Desk Support | $25 – $75 per user |
| Cloud Services | $50 – $300 per user |
By utilizing this chart, businesses can create a more informed budget plan that accurately reflects the costs associated with each service, mitigating the risk of unexpected expenses. Understanding these details not only supports better financial planning but also enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of IT management.
Trends in MSP Pricing
The landscape of Managed Service Provider (MSP) pricing is evolving rapidly, particularly with the integration of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions. As technology advances and businesses increasingly rely on cloud-based services, MSPs are rethinking their pricing strategies to accommodate new service demands and enhance customer satisfaction. This evolution not only reflects the changing needs of clients but also showcases the competitive nature of the MSP industry.One of the most significant trends in the MSP pricing landscape is the shift towards subscription-based models.
This trend allows companies to predict and manage their IT budgets effectively while providing MSPs with a more stable income stream. The integration of RMM solutions has further facilitated this shift by enabling providers to offer a range of services under one umbrella, thereby simplifying the purchasing decision for clients. In addition, the adoption of tiered pricing models is becoming increasingly popular, allowing customers to select service levels that align with their specific needs and budget constraints.
Innovative Pricing Strategies
As MSPs adapt to the changing market conditions, several innovative pricing strategies have emerged. These strategies are designed to enhance service delivery, improve customer retention, and align with the financial expectations of clients. Notable examples include:
- Usage-Based Pricing: Some MSPs are now implementing pricing models based on actual usage of services rather than flat fees. This approach allows clients to pay for only what they consume, which can lead to significant cost savings, especially for businesses with fluctuating IT needs.
- Value-Based Pricing: Instead of traditional cost-plus methods, leading MSPs are shifting towards pricing based on the value delivered to the client. This model focuses on the outcomes and business impact of the services provided, ensuring that clients feel they are receiving tangible benefits from their investment.
- Bundled Services: Many MSPs are offering packages that combine multiple services at a discounted rate. This not only simplifies the purchasing process for clients but also encourages them to utilize a broader range of services, which can enhance their overall IT experience.
Timeline of MSP Pricing Model Changes
Over the past decade, the MSP pricing models have undergone significant transformations, reflecting technological advancements and changing business needs. The following timeline highlights key developments in MSP pricing strategies:
| Year | Change in Pricing Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Introduction of Flat-Rate Pricing | MSPs began offering predictable monthly fees for a set range of services, shifting away from hourly billing. |
| 2015 | Adoption of RMM Solutions | The rise of RMM tools allowed MSPs to proactively manage client systems, enhancing service quality and justifying subscription pricing. |
| 2017 | Shift to Tiered Pricing | MSPs started implementing tiered service levels, enabling clients to select packages that matched their specific needs and budget. |
| 2020 | Increased Focus on Cybersecurity | With the growing threat of cyber attacks, MSPs began to incorporate cybersecurity services into their pricing models, often as premium offerings. |
| 2023 | Emphasis on Value-Based Pricing | MSPs are increasingly focusing on the value delivered to clients, moving away from traditional cost-based pricing models. |