Monthly RMM Reports sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. These reports are essential for IT management, serving as vital tools that track performance and service delivery. By encapsulating key metrics, they provide an overview of system health and operational efficiency, ensuring that businesses can make informed decisions based on solid data.
Furthermore, the components of an effective Monthly RMM Report are meticulously crafted, incorporating structured data formats like HTML tables and enhanced clarity through visual aids such as graphs and charts. This makes the data not only easier to digest but also visually appealing, facilitating better communication among stakeholders.
Importance of Monthly RMM Reports

Monthly RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) reports are essential tools in IT management that provide organizations with insights into their technological performance and health. These reports not only highlight current system status but also pave the way for informed decision-making, resource allocation, and proactive planning. By regularly reviewing these reports, businesses can maintain operational efficiency and ensure their IT infrastructure is aligned with organizational goals.The significance of monthly RMM reports lies in their ability to track performance metrics, uncover trends, and facilitate strategic adjustments.
These reports serve as a compass, guiding IT managers and stakeholders in understanding how well their systems are functioning and where improvements may be necessary. A thorough analysis of RMM reports allows organizations to react to issues swiftly, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall service delivery.
The finance sector is undergoing significant transformation with the implementation of RMM. By leveraging Finance Sector RMM , institutions can enhance their risk management strategies and streamline operations, ultimately driving profitability and efficiency. This integration not only addresses contemporary challenges but also positions financial entities to adapt to an evolving market landscape.
Key Metrics in Monthly RMM Reports
Incorporating key performance indicators (KPIs) into monthly RMM reports is crucial for evaluating IT effectiveness. These metrics provide a clear picture of system performance and can highlight areas requiring attention. The following are significant metrics commonly included in these reports:
- System Uptime: This metric measures the reliability and availability of IT systems. A high uptime percentage indicates that systems are functioning properly, which is vital for uninterrupted business operations.
- Incident Response Times: Tracking how quickly IT teams address and resolve incidents can reflect the efficiency of support services. Shorter response times can lead to improved user satisfaction and reduced disruption.
- Patch Management Compliance: Regular updates and patches are essential for security and performance. This metric assesses the percentage of systems that are up-to-date, ensuring vulnerabilities are minimized.
- Resource Utilization: Understanding how effectively resources like CPU, memory, and storage are being utilized can help identify potential bottlenecks and optimize system performance.
- User Satisfaction Scores: Collecting feedback from end-users can provide insights into how well IT services are performing and highlight areas for improvement.
The integration of these metrics into monthly reports enables IT leaders to monitor health indicators and adjust strategies to foster a more robust IT environment.
“Regular evaluation of RMM metrics not only ensures system health but also empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions.”
In the realm of manufacturing, the adoption of RMM is proving to be a game-changer. Companies are utilizing Manufacturing with RMM to optimize production processes and reduce waste, fostering a more sustainable and efficient operation. This innovative approach allows manufacturers to stay competitive while meeting the growing demands of the industry.
Components of Effective Monthly RMM Reports
Monthly Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) reports serve as vital tools for organizations to assess the performance and health of their IT systems. An effective RMM report not only summarizes essential data but also highlights areas needing attention, ensuring that teams can act proactively. A well-structured report encompasses various components that allow stakeholders to derive meaningful insights quickly.To ensure clarity and comprehensiveness in reporting, certain key elements must be included.
These elements should be systematically organized to facilitate easy interpretation and decision-making. The following are essential components that contribute to the effectiveness of monthly RMM reports:
Essential Elements of Monthly RMM Reports
The inclusion of specific elements in monthly RMM reports is crucial for providing a complete view of the IT environment. Below are the critical components that should be addressed:
- Executive Summary: This section provides a high-level overview of the report’s findings, summarizing critical data and highlighting significant trends or issues.
- System Performance Metrics: Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as uptime, response times, and resource utilization should be detailed to assess system efficiency.
- Incident and Issue Tracking: A summary of incidents and issues resolved during the month, including their impact and resolution timeframes, helps track the effectiveness of support services.
- Security Status: Current security incidents, vulnerabilities, and updates on anti-virus and malware protections should be reported to ensure the IT infrastructure’s safety.
- Action Items and Recommendations: A section that Artikels necessary actions based on the report’s findings, ensuring timely follow-up on any identified issues or improvements.
- Client Feedback: Including feedback from clients about the services received can provide valuable insights for ongoing improvement.
Data Presentation Format Using HTML Tables
Utilizing structured formats, such as HTML tables, allows for a clear presentation of data within monthly RMM reports. Organizing information in table format enhances readability and allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the data’s significance.Here is an example of a structured HTML table format representing system performance metrics:
| Metric | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uptime | 99.9% | 99.8% | 99.95% |
| Average Response Time | 120 ms | 130 ms | 115 ms |
| Resource Utilization | 70% | 75% | 68% |
This structured presentation allows for quick comparisons across different months, making it easier to identify trends or anomalies in system performance.
The Role of Visual Aids in Enhancing Report Clarity
Incorporating visual aids such as graphs and charts within monthly RMM reports significantly improves clarity and engagement. Visual representations of data allow stakeholders to quickly interpret complex information and identify trends at a glance.Bar charts can effectively illustrate comparisons between different performance metrics over time. For instance, a bar chart showing incident response times can quickly convey improvements or deteriorations in service quality.
Pie charts can represent security status, providing immediate visibility into the proportion of incidents resolved versus those still open.
“Visual aids not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of reports but also improve the retention of information by presenting data in an easily digestible format.”
Overall, the strategic combination of essential report components, structured data presentation, and compelling visual aids ensures that monthly RMM reports are not only informative but also actionable.
Best Practices for Creating Monthly RMM Reports
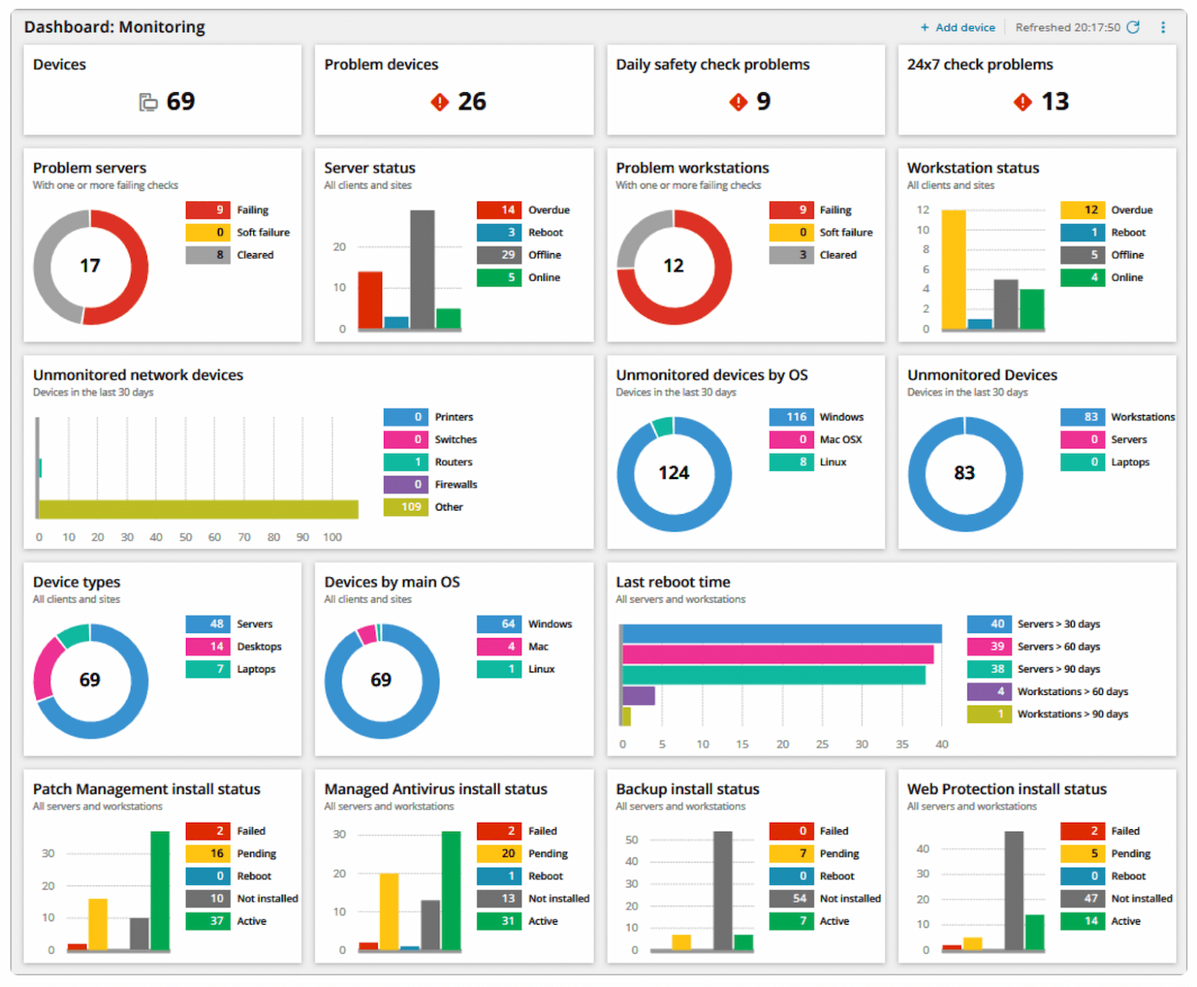
Creating effective Monthly Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) Reports is essential for maintaining transparency and facilitating informed decision-making. By adhering to best practices in compiling and formatting these reports, organizations can significantly enhance their communication with stakeholders.Effective reporting involves not only presenting data but also ensuring that it is easily digestible and tailored to the audience’s needs. Following best practices helps to streamline the process, making reports both comprehensive and actionable.
Compiling and Formatting Data
Organizing data in a clear and concise manner is crucial for the success of Monthly RMM Reports. The following best practices are key to achieving this:
- Utilize visual aids such as charts and graphs to represent data trends effectively, making it easier for readers to grasp complex information at a glance.
- Maintain a consistent format throughout the report, with uniform headings, font styles, and colors to promote readability and professionalism.
- Incorporate relevant metrics, such as system uptime, incident response times, and customer satisfaction scores, to provide a comprehensive overview of performance.
Checklist for Finalizing Reports
Before finalizing Monthly RMM Reports, it is essential to review specific components to ensure accuracy and completeness. This checklist can help:
- Verify that all data sources are accurate and up-to-date.
- Ensure that key performance indicators (KPIs) are included and clearly highlighted.
- Confirm that all visual aids are correctly labeled and referenced in the text.
- Review for grammatical errors and ensure consistency in terminology.
- Seek feedback from team members or stakeholders to enhance the report’s clarity and utility.
Customizing Reports for Stakeholders
Different stakeholders require different types of information, and customizing reports accordingly can significantly enhance their effectiveness. Here’s how to tailor reports for various audiences:
- For clients, focus on metrics that highlight service value, such as uptime percentages and response times, along with detailed narrative insights to explain these figures.
- For internal teams, include operational details, such as troubleshooting case studies and improvement strategies, which can help in knowledge sharing and process enhancement.
- For executive management, present high-level summaries with essential metrics and strategic insights, emphasizing overall performance and future growth potential.
“Customizing reports not only improves stakeholder engagement but also enhances the overall effectiveness of communication.”
Challenges in Generating Monthly RMM Reports
Generating Monthly Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) reports is a critical task for IT service providers, enabling them to assess and communicate the performance and health of client systems. However, various challenges can impede the efficiency and accuracy of these reports. Addressing these challenges is essential to ensure that the reports deliver actionable insights and maintain client trust.One of the primary issues encountered when generating monthly RMM reports is data discrepancies.
These discrepancies can arise from multiple sources, including inconsistent data entry, variations in data formats, and integration challenges between different tools and platforms. Additionally, reporting errors may stem from human oversight during manual reporting processes, leading to inaccuracies that can misinform decision-making.
Common Issues Encountered in RMM Reporting
The following points detail some of the most common challenges faced during the reporting process:
- Data Inconsistency: Variations in how data is collected or entered can lead to conflicting reports.
- Integration Problems: Difficulty in integrating data from various monitoring tools can result in incomplete or erroneous information.
- Time Constraints: Limited time for report generation often leads to rushed and error-prone work.
- Overlooking Key Metrics: Important performance indicators may be missed in reports, affecting strategic planning.
- Human Error: Manual entry or calculation mistakes can compromise the report’s integrity.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach. Implementing solutions for data discrepancies is vital. Regular training for staff on data input standards and utilizing standardized reporting formats can significantly reduce inconsistencies. Additionally, frequent audits and validations of the data can help identify and correct errors before reports are finalized.
Solutions for Data Discrepancies and Reporting Errors
To effectively tackle discrepancies and errors in RMM reports, consider the following solutions:
- Automated Data Collection: Employ automation tools to gather and consolidate data, reducing human intervention and potential errors.
- Regular Data Audits: Schedule periodic checks of data integrity to identify inconsistencies early in the reporting process.
- Standard Operating Procedures: Develop and enforce standard procedures for data entry and reporting, ensuring consistency across the board.
- Real-time Monitoring: Implement systems that provide real-time data updates to reduce discrepancies from outdated information.
Comparison of Manual and Automated Reporting Processes
The choice between manual and automated reporting processes significantly impacts efficiency and accuracy. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach can guide organizations in selecting the best method for their needs.
- Efficiency: Automated reporting processes can generate reports at a much faster pace than manual methods. This not only saves time but also allows for more frequent reporting.
- Accuracy: Automation minimizes the risk of human error commonly associated with manual data entry and calculations, resulting in more reliable reports.
- Consistency: Automated systems use preset templates and standard metrics, which helps maintain consistency across reports.
- Resource Allocation: By reducing the time spent on report generation, teams can allocate resources to other critical tasks, enhancing overall productivity.
In summary, the challenges in generating monthly RMM reports stem from data discrepancies, reporting errors, and the choice between manual and automated processes. By implementing effective solutions and recognizing the advantages of automation, organizations can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of their reporting efforts.